HomeHistory
History of Our Land “सिन्ध سنڌ Sindh “
Geographical Information
The ranges of the Hindu Kush, the Karakoram and the Himalayas separate South Asia from the rest of Asia. The Indus ( Sindhu) , the Ganges and the Brahmaputra rivers flowing through the plains.
The Asian subcontinent was part of the ocean bed with a ring of mountains acting as a barrier of cliff-shored islands. With time as the ocean regressed; the bed developed into a fertile plain. The rivers found a way to end into the distant ocean. The Indus (Sindhu) River was the longest of the three great sub-continental rivers – the Indus (Sindhu), Ganga and Brahmaputra.
The Indus River is the ‘Sindhu’ Nadee ‘ or the ‘Puranik’ (meaning Ancient) river. Hindu religion get their names from the word “ Sindhu ( pronounced as Hindu) “ River. Ironically, it became famous name of the country “Hindu sthan “. Thus the religion of the people who live by its Shores called “Hindu” . The language called Hindi which is taken from HIM NADEE . These rivers collect water from several streams flowing from the mountains of Himalaya, Tibet, the Soviet Union, and Afghanistan.
Five major rivers flow from the Sindhu Nadi (River) - the Jhelum, Chenab, Ravi, Sutlej, and Beas. History of Sindh revolves around the people who lived along these waters and those in the Desserts deprived of its waters.
Discovery of a Old Civilization

The word ‘Sindh’ emerges from the word (Seendh سينڌ ) means the middle parting of the head dividing the hair into two parts. It also derives references from the powder; Sindoor; applied by married Hindu ladies on their head.
With time, Seendh سينڌ developed into Sindh and the Sindhu River, became the lifeline of people living on both the sides of the river. The people were historically, linguistically, and culturally diverse. They spoke Sindhi, Punjabi, Pashto and Balochi as well as Katchi and Gujarati. This was due to the cultural fusion and clash of fifty-five countless centuries of civilization.
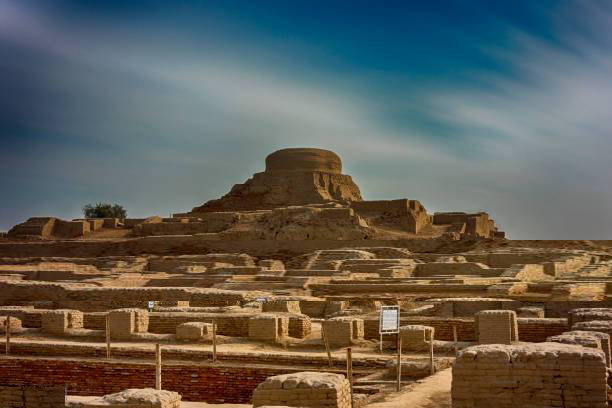
In the 1920s, an expedition of the Indian Archaeological Survey under Sir John Marshall unearthed a thought-provoking mound of earth in the Sindh region of the then British India. The locals called this earthy protuberance Mohan-jo-Daro. The literal meaning being ‘Muhinjo Dharo’ meaning ‘My City’ or ‘My Palace’.
Along with the discovery of Mohan-jo-Daro , Further investigations and studies unearthed other well-developed cities. Harappa, Chanhu-Daro, Lothal, and Kot Digi cities mark the beginning of the civilization. Beginning as early as 3000 BC attaining its zenith by 2000 + BC, and assuming perished by 1000 BC.
The remains of the Mohan-jo-Daro spoke volumes of the state of affairs from the civilization point of view all through the period. These people were the Aryans from the time of Ramayana when Bhagwan Shree Ram travelled from north to south - Kanyakumari and farther went to Lanka, an island. He conquered the island by killing king Ravana.
The Indus valley finds its mention in history - the battle of Hastinapur (Mahabharat) when king Jaidrath engaged his army to support the Kauravs with Pandavs. Bhagwan Shree Krishna was in full support of the Pandavs on the battlefield.
The Bhagwad Geeta (meaning ‘song of God’) encapsulates Shree Krishna’s advice to the famous Pandav warrior Arjun in dialogue form. Wherein, he guides the dejected Arjun to fight for his right against his cousins. The Bhagwad Geeta is for all who lose life’s vision as it revolves around – knowledge, action and love.
The arrival of Arabs/Moguls
The Sindhis ruled the Sindh . The Arabs travelled Sindh for business purpose for food grains, fruits, vegetables, spices as the Arabistan was a desert and less cultivable. As a result, they exchanged food items with Pearls, Fish and Khajoor (Dates).
Their continuous visits caused them to settle in the Sindh region. Arab left their slaves to collect the seasonal items. When they lived for long time they marry the local Sindhi Girls / Boys
Many of them were Muslims who worked as laborers, cleaners, and in the fields fetching water from wells and rivers for selling and make their livelihood. They worked under the Zamindars or Vadera as servants.
In select regions, some Muslims proclaimed themselves as rulers even though they were not the rightful rulers. Many of them were Hindus-converted to Islam while many by marriage to the local Sindhi girls and boys. This gave shape to a heterogeneous society that lived in peace and harmony.
The Sindhi rulers ruled until the Muslims gained majority by conversion or by marriage. Rise of a New Language Arabic and Farsee mingled with Sindhi, Punjabi and Hindi and formed ‘Urdu’. Urdu or ‘Aur Do’. literally means a mix of local languages (Hindi / Punjabi/ Gujrati ) with two other languages - Arabic and Farsee. But they adopted Farsee script since most of the slaves brought were from Iran (Persia).
Religion
At that time there were many Sindhi Hindu saints with a vast knowledge of Vedas, Upanishads,Purans, Ramayan and the Mahabharat (Geeta Gyan).
The saints became popular with Muslims too; turning them into followers. With time, their Religion known as Suffee Mixture of Hindu muslim thoughts. The influence of Hinduism and the Islamic religion gave rise to a contemporary faith – Sufism. However, some Muslim tribals initiated atrocities by forcing the Hindus to convert to Islam.
One of Sindhi Saint named Sant Kanwar Ram . One of His historic miracle is when he unknowingly brought a dead child back to life in his arms while he sang a ‘Lori’ lullaby. He stopped singing Lori when he realised the child in his arms was dead. And felt guilty of interrupting God’s will ‘Bhagwan’s work’ and brought a dead child to life.
Some Muslims fanatic could not believe the miracles of one such saint - Sant Kanwar Ram. Later, few fanatic decided to assassinate Sant Kanwar Ram. One day at RUK railway station in Sindh they shot dead Sant Kanwarram. This was a great blow to their belief of brotherhood in Muslim community.
During partition of India in the year 1947 Hindus 75% (Sindhi, Punjabi, Marwaree, Gujrati ) left the Sindh place to spread and settled down in various parts of India. The remaining 25% Hindus who remained in Pakistan ( some of East & West portion given to Muslim). Were never given equal rights in Pakistan . Hence they were treated as outsiders in their own native place. Later on most of them (Men) were either converted to accept Islam or killed and ladies were forced to marry with slaves (Pakistanis) or tortured and killed .